
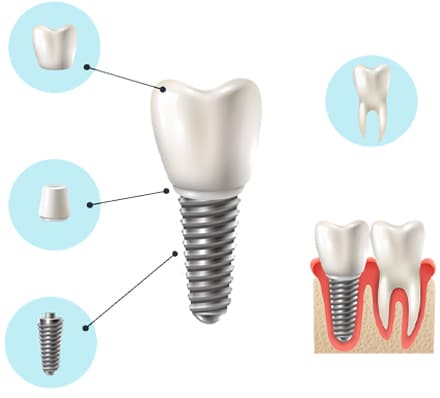
The dental implants function as an artificial titanium root, which is placed in the jawbone or mandible, and a process of integration takes place in the area called osseointegration.
When the absence is individual, we place an implant, with a crown attached to it, forming a structure similar to that of a tooth, and with the same aesthetics as your natural dentition.
When several teeth, or the whole arch, are missing, we will consider the best option in the distribution of the implants to place the prosthesis on top (implant-supported).
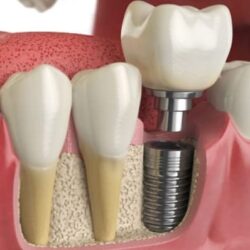
What are dental implants?
Dental implants are the best option for replacing one or more missing teeth, restoring both aesthetics and function.
These are prosthetic attachments, made of biocompatible materials such as titanium or zirconium, which are screwed into the maxillary or mandibular bone to replace the root and place a restoration over them.
The dental implant is firmly attached to the bone by a mechanical and biological lock in a process called osseointegration. This keeps the implant securely in position and ensures its success.

When a single tooth is to be restored, a crown is placed on the implant. This combination has the characteristic of feeling very similar to a natural tooth as it has a similar structure.
On the other hand, these crowns are made in the same colour as the natural teeth. In this way, a harmonious and discreet result is achieved.
However, dental implants can also be used to replace multiple teeth in cases of extensive tooth loss, including an entire arch. In these cases, a meticulous evaluation is performed to determine the best position for the implants and to place a prosthesis on them.
Steps to implant placement
There are different protocols for implant placement. However, the most common involves the following steps:
1. Planning
A thorough clinical and radiographic evaluation is performed to determine the position of the implant and to analyse anatomical structures of interest, such as the location of the dental nerve and the floor of the maxillary sinus.
2. Pre-prosthetic fitting
Occasionally, the bone requires extra preparations prior to implant surgery.
One of the most common is bone grafting, which is used when there is not enough bone to safely place the implant. However, this step is not always necessary and is inherent to the characteristics of the case.
3. Implant surgery
First, an incision is made in the gum to expose the bone and the implant is placed in the planned position.
The gum is then sutured over the implant, covering it completely while the healthy area and the implant integrates with the bone. This osseointegration process can take 3 to 6 months to complete.
4. Unclogging surgery and placement of healing abutment.
Once osseointegration is complete, a small incision is made in the gum to expose the implant and an attachment called a healing abutment is screwed to it.
This helps the gum to heal into the desired shape before the crown is placed.
5. Final abutment and temporary crown
The healing abutment is replaced by a definitive abutment. This is an attachment that is screwed to the implant and on which the crown will be placed.
A dental impression is taken for the final crown to be made in the laboratory and a temporary crown is placed.
6. Placement of the final crown
Once the definitive crown is in place, the temporary crown is replaced by this one, concluding the case.

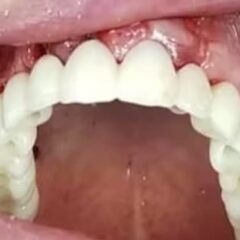
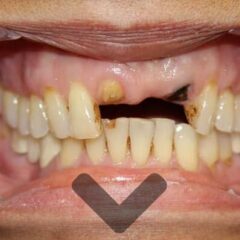
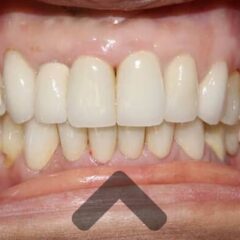
Advantages of Implants
Dental implants have many features that make them the best option, such as:
- Comfort: They feel similar to natural teeth.
- Rapid adaptation: It is easier to get used to eating and speaking with an implant-supported prosthesis than with a gum-supported prosthesis.
- Conservative design: There is no need to wear down other teeth as when a fixed bridge or a removable partial denture is installed.
- Aesthetics: the result of treatment with implants is highly aesthetic, achieving finishes equal to natural teeth.
There is no more natural alternative than an implant to replace a missing tooth. Make an appointment and let us give you back your smile.


